Level 1 CFA® Exam:
Macroeconomics - Advanced
Long-Run Full Employment vs Short-Run Recessionary Gap vs Short-Run Inflationary Gap vs Short-Run Stagflation
star content check off when doneLong-Run Full Employment
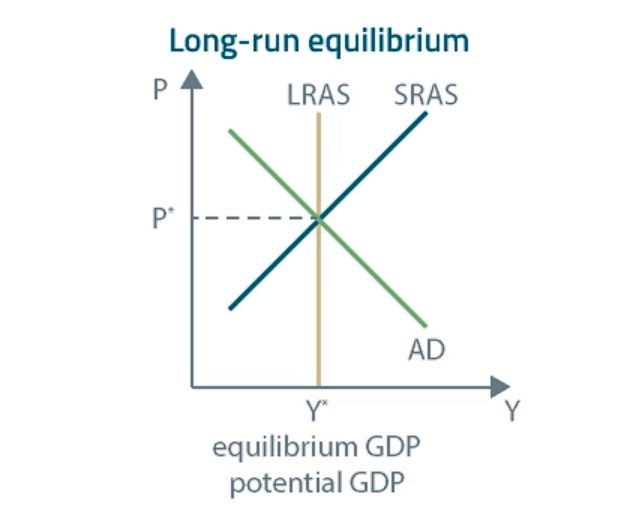
The graph above presents a situation in which the economy is in the long-run full employment. As you can see, for the long-run full employment, the AD curve, short-run AS curve, and long-run AS curve intersect at the same point. At this point, equilibrium GDP is equal to potential GDP.
However, as we learned in the previous lesson, shifts in AD and SRAS curves are possible. What happens if either the AD or the SRAS curve shifts?
There are mainly 3 situations possible. We may deal with:
- short-run recessionary gap,
- short-run inflationary gap, or with
- short-run stagflation.
The first two are effects of AD curve shifts, while short-run stagflation results from the shift in the short-run AS curve.
Short-Run Recessionary Gap
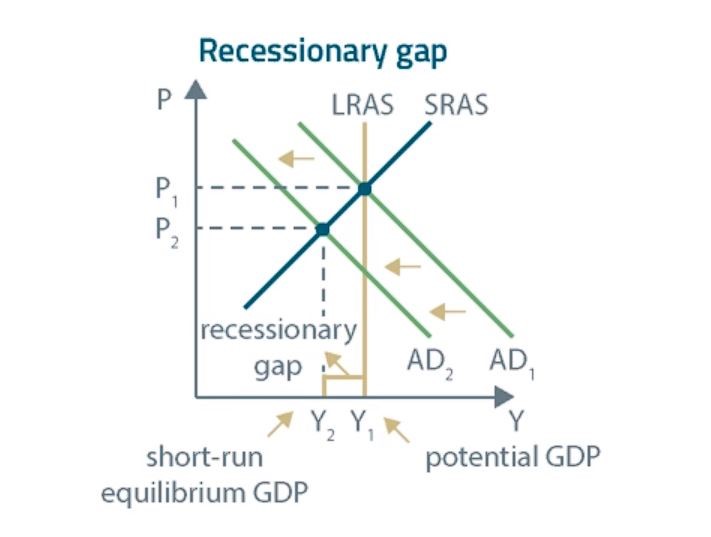
A short-run recessionary gap occurs when the AD curve gets shifted to the LEFT.
If we deal with a recessionary gap, a short-run equilibrium GDP is lower than the potential GDP. The greater the difference between the potential GDP and equilibrium GDP, the greater the recessionary gap.
Short-Run Inflationary Gap
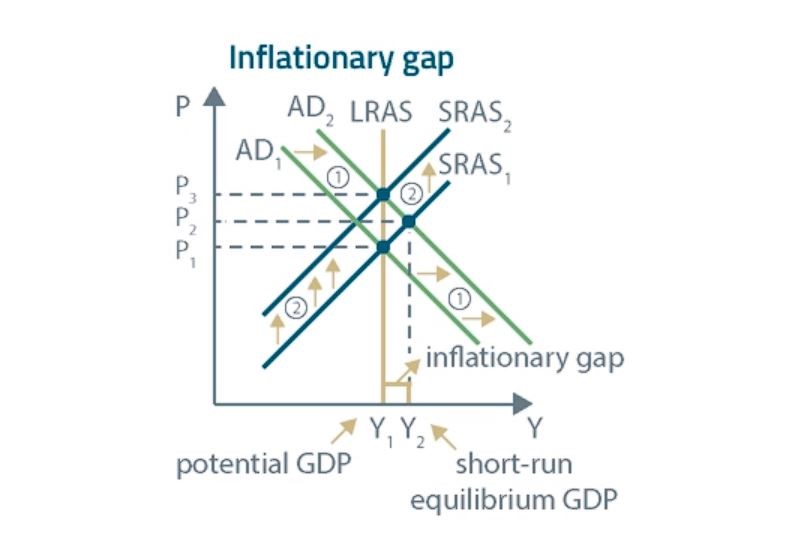
(...)
Short-Run Stagflation
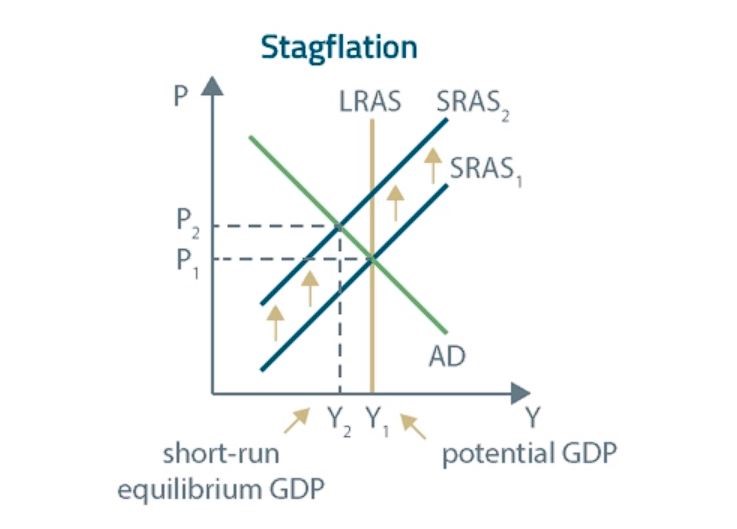
Let’s analyze what happens when aggregate supply falls.
If the short-run AS curve shifts to the LEFT, we will deal with both high inflation and high unemployment. This situation is called stagflation. As you can see in the graph, equilibrium GDP is below potential GDP, which means that there is no full employment. Also, the price level has risen.
Now, we will have a look at the effects of simultaneous changes in aggregate demand and aggregate supply. 4 variants are possible:
- Both the aggregate supply and the aggregate demand increase.
- Both the aggregate supply and the aggregate demand decrease.
- The aggregate supply increases and the aggregate demand decreases.
- The aggregate supply decreases and the aggregate demand increases.
(...)
Sources of Economic Growth
The basic sources of economic growth include:
- labor supply,
- human capital,
- physical capital,
- technology, and
- natural resources.
Labor supply is made up of the entire labor force, that is of all people of working age that are either employed or unemployed but available to work. Labour supply is shaped by such determinants as the birth rate or migration balance.
Human capital, alongside the potential of the workforce, is an important determinant of economic growth. More specifically, it's about the quality of human capital which is determined by education and skills and translates into greater productivity of labor and smoother adaptation to technological changes.
Physical capital stock includes such resources as buildings, machinery, and equipment. It depends on net investment, that is gross investments minus depreciation. It increases if gross investments exceed depreciation. Countries with a positive level of net investment have a higher rate of economic growth.
As for technology, its development results in greater productivity and contributes to increasing potential GDP.
Economic growth also depends on the quantity of renewable and non-renewable natural resources, such as crude oil, soil, or water.
The Solow growth model helps us understand how economic growth works.
According to the Solow growth model, the production function shows the relationship between output, on the one hand, and labor, capital, and their productivity, on the other hand:
(...)
We can also derive the growth in (per capita potential GDP):
Growth in (per capita potential GDP) equals (growth in technology) plus (growth in the capital-to-labor ratio) times (the share of capital in national income).
Other formulas that might be useful in your exam:
- For the long-run full employment, the AD curve, short-run AS curve, and long-run AS curve intersect at the same point.
- A short-run recessionary gap occurs when the AD curve gets shifted to the LEFT.
- A short-run inflationary gap occurs when the AD curve gets shifted to the RIGHT.
- If the short-run AS curve shifts to the LEFT, we will deal with both high inflation and high unemployment. This situation is called stagflation.
- The basic sources of economic growth include: labor supply, human capital, physical capital, technology, and natural resources.
- According to the Solow growth model, the production function shows the relationship between output, on the one hand, and labor, capital, and their productivity, on the other hand.


