Level 1 CFA® Exam:
Risk Management Framework
Here are risk-related definitions you should know in your level 1 CFA exam:
- risk = exposure to uncertainty,
- risk exposures = how much a company or an individual taking risks is exposed to these risks; state of being exposed to risk,
- risk drivers = fundamental factors that are potential sources of risks for a company or an individual,
- risk management = the process used by a company or an individual to define, measure, adjust to, and monitor the risk being taken to maximize the company’s value or the individual’s utility; risk management is not the same as avoiding risk, it’s rather about taking risk actively and knowingly,
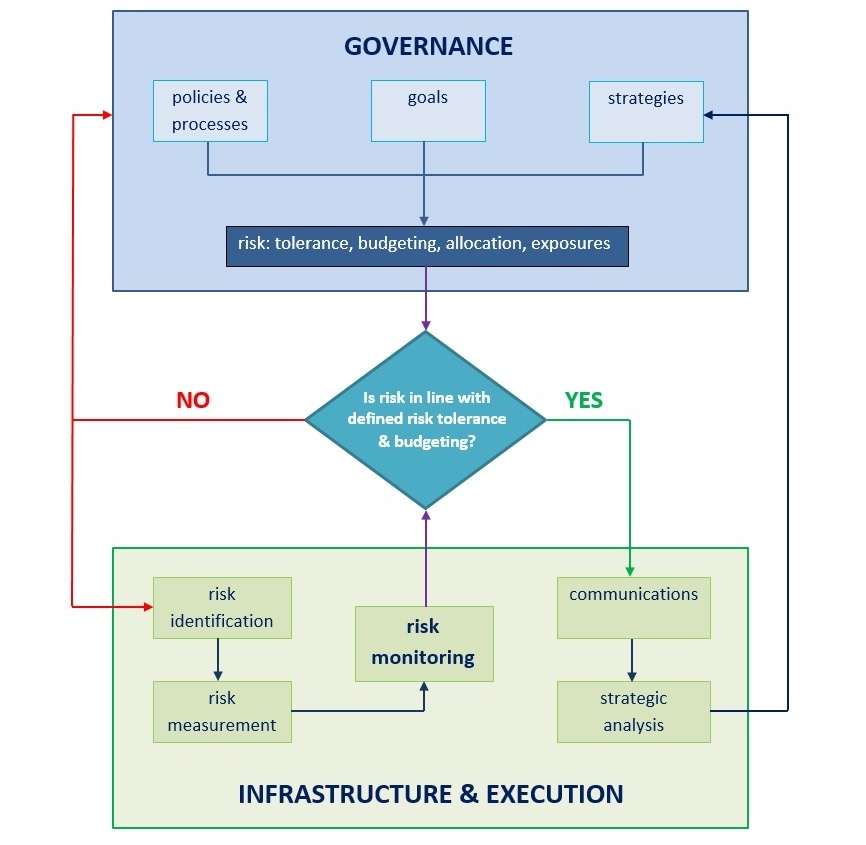
- risk governance = the top-down process that helps define risk tolerance, oversees risks and goals, and provides guidance for risk management,
- risk tolerance = entity’s risk appetite (how much loss it is ready to accept) + deciding which risks are acceptable and which are not,
- risk budgeting = allocates the entity’s tolerable risk by specific metrics,
- risk identification and measurement = quantitative core of risk management + qualitative assessment of potential risk drivers and exposures affecting an enterprise,
- risk infrastructure = people and systems required to do quantitative tasks related to risk management and covering topics like risk measurement, risk monitoring, tracking of risk exposures, and assessment of the company’s risk profile,
- defined policies and processes = extension of risk governance focusing on everyday policies and processes related to risk management,
- risk monitoring, mitigation, and management = here 'main work' happens; we take risk governance, risk identification and measurement, risk infrastructure, and defined policies and processes to monitor, mitigate, and manage risks and align risk exposures with defined risk tolerance; also we have to make sure to factor in changing risk drivers and risk exposures,
- communications = communication of risk-related issues across all levels of the company including feedback loops, continuity and timeliness of the information, and review and discussion of risk-related topics,
- strategic analysis and integrations = taking into account the big picture, deciding what works and what does not, and what brings the most value per amount of risk taken.
- Risk is exposure to uncertainty.
- Risk management is a process used by a company or an individual to define, measure, adjust to, and monitor the risk being taken to maximize the company’s value or the individual’s utility.

